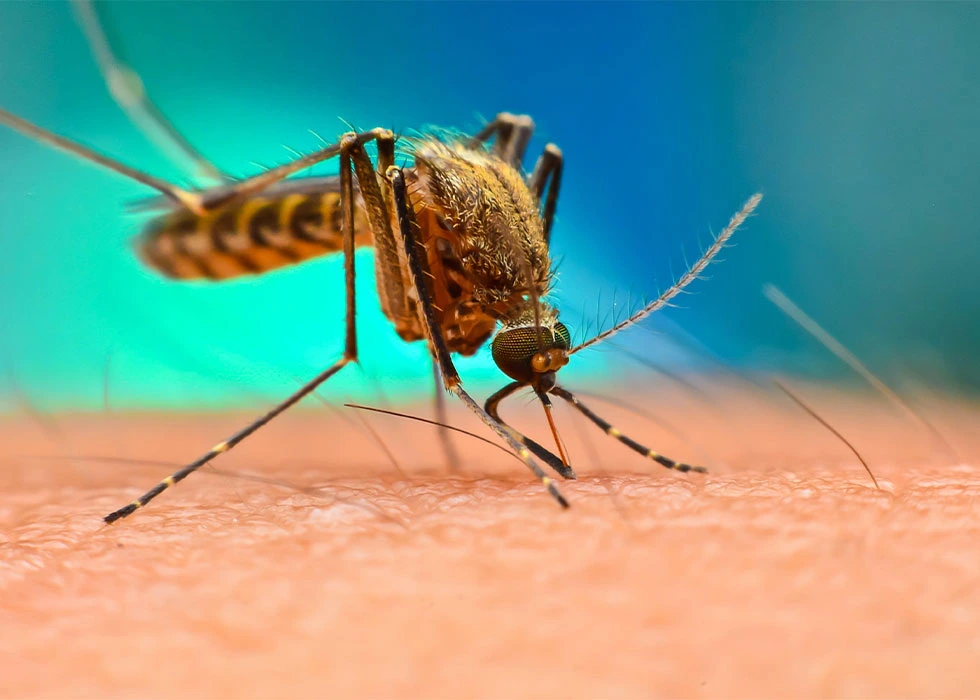
Malaria is one of the world’s most widespread and dangerous infectious diseases. It is caused by Plasmodium parasites and spreads through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. While it is rare in the United States and Europe, malaria remains a major global health challenge, with hundreds of m...
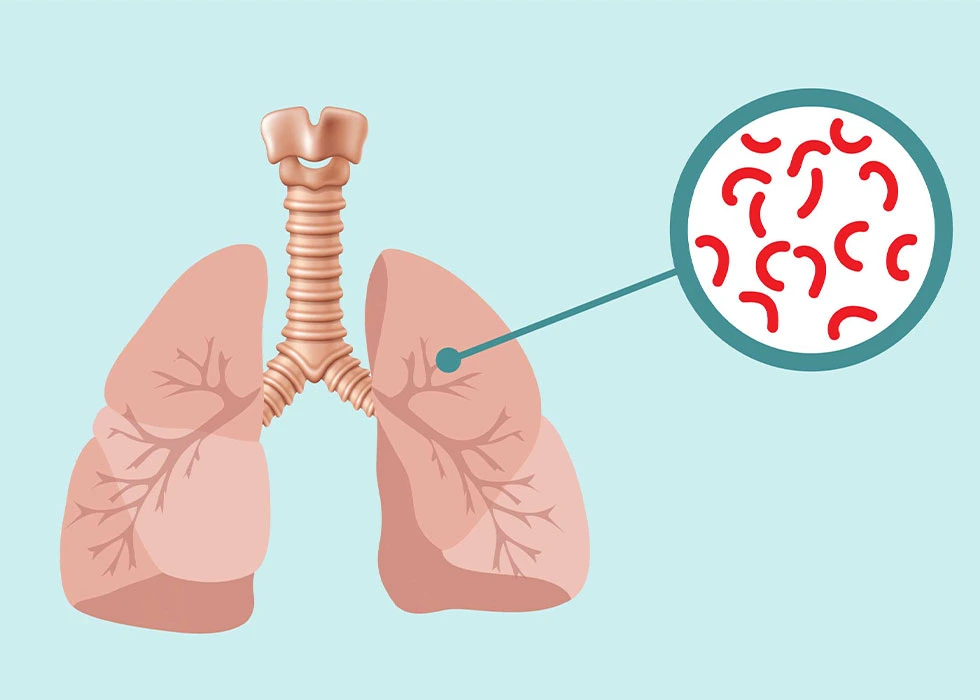
Tuberculosis (TB) is an ancient disease that continues to affect millions of people around the world. Caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis, TB most commonly attacks the lungs, but it can also spread to other organs such as the brain, spine, or kidneys. While it was once the leading cause of death in th...

HIV and AIDS are often mentioned together, but they’re not the same thing. HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. If left untreated, it can lead to AIDS, which is the most advanced stage of HIV infection. With modern treatment, however, HIV is now considered...

Influenza, more commonly known as the flu, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. Unlike the “stomach flu,” which refers to gastroenteritis, true influenza attacks the respiratory system—the nose, throat, and lungs. While many people recover within a week or two, the flu can sometimes...
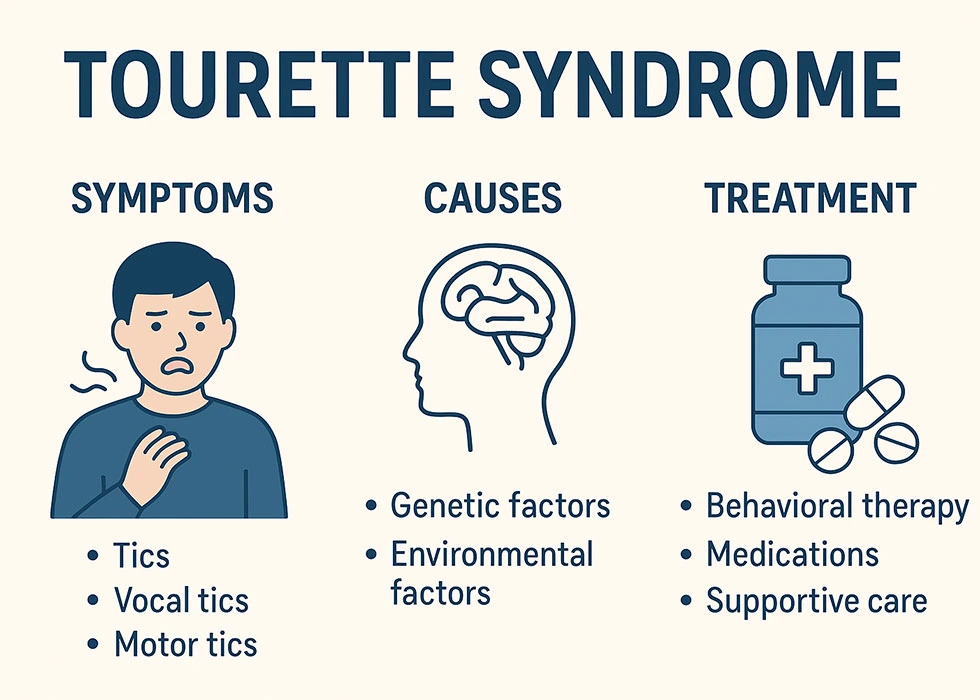
Tourette Syndrome (TS) is a neurological disorder that affects the brain and nervous system, leading to sudden, repetitive movements or sounds called tics. These tics are involuntary — meaning people can’t fully control them — and often begin in childhood. While the condition may sound intimidating, most peop...